The Role of IoT in Connected Vehicle Technology
Imagine your car could warn you about an upcoming traffic jam, suggest alternate routes, automatically dial emergency services after an accident, or even tell your coffee machine to start brewing as you're pulling into your driveway. This is not a glimpse into a science fiction movie, but rather the reality of the Internet of Things (IoT) integrated into connected vehicle technology.
In 2020 alone, 91% of all passenger cars sold in the U.S. were connected. This tells us over the next decade connectivity will fundamentally change the car experience. And IoT is playing a big role in ensuring that connected vehicles become truly ‘smart’.
Understanding IoT and Connected Vehicle Technology
Before diving into the specifics, it's essential to understand what we mean by IoT and connected vehicle technology. The Internet of Things refers to a network of interconnected devices and objects that collect and exchange data. When applied to vehicles, it means cars become more than just a mode of transportation; they transform into smart devices with advanced functionalities.
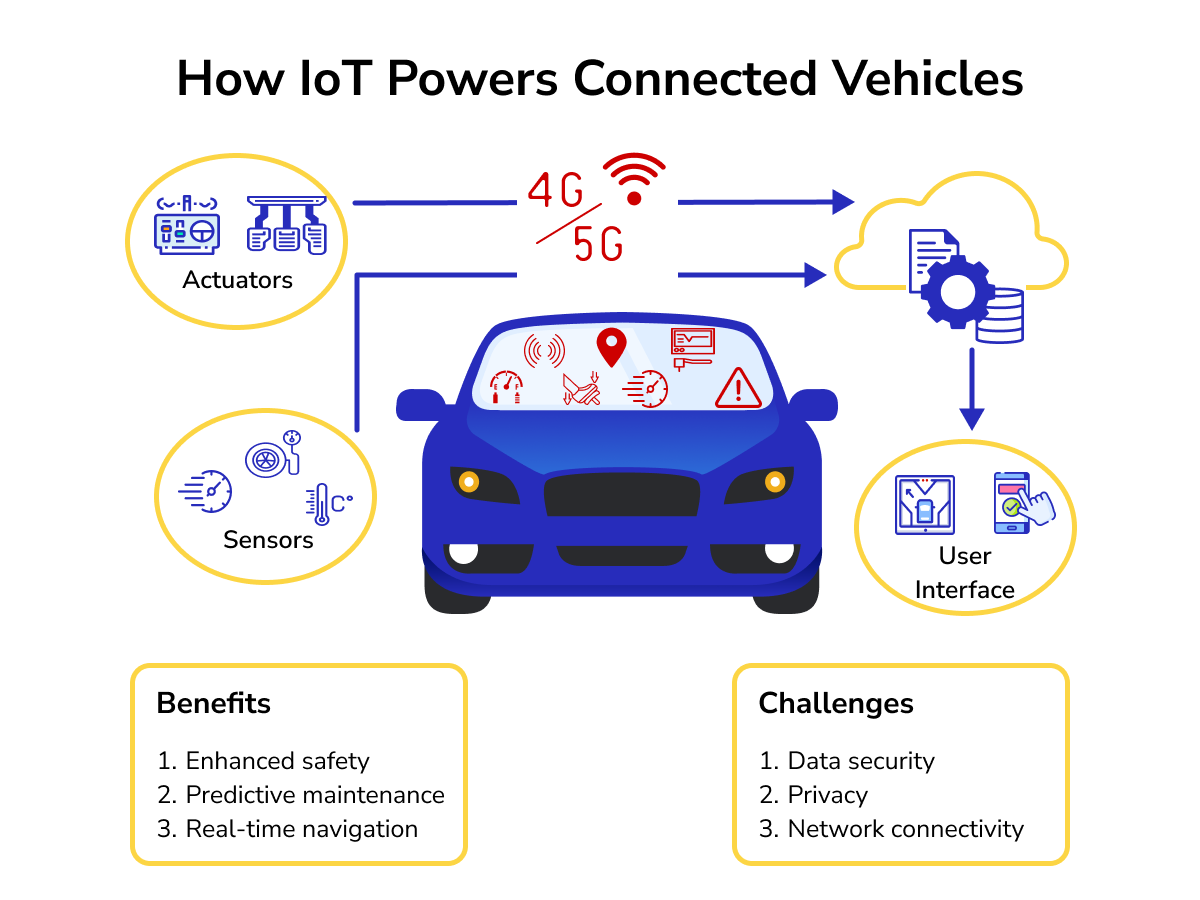
The application of IoT in vehicles has brought forth innovative features, including predictive maintenance using telematics data, real-time navigation and traffic updates, enhanced safety features like automatic emergency braking (AEB), and personalized in-car services.
For instance, Tesla, one of the front-runners in connected vehicle technology, employs IoT to offer features such as Autopilot and over-the-air (OTA) updates that continuously improve vehicle functionality without the need for physical service.
The other example of this is the recent Mercedes Benz recall, wherein the dealership had to physically update the software in all affected vehicles. This could have been easily avoided had the vehicles been equipped with IoT features such as over-the-air updates.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
We may think that IoT is the obvious next step in automotive tech. However, integrating IoT into vehicles isn't without challenges. Here are some concerns that plague the connected vehicle industry.
Data Privacy and Security: Connected vehicles generate and transmit a lot of data, such as your location, driving habits, and even personal information like contacts if your phone is linked. This could be a problem if the data were to fall into the wrong hands, as it could be misused.
Solution: To protect against misuse of data, car manufacturers and tech companies are strengthening their cybersecurity measures. Think of these as super advanced locks and alarms that are designed to keep the bad guys out of your data.
Network Connectivity: Just like how your phone sometimes loses its internet connection in certain areas, connected cars can face the same issue. If a car relies on a data connection for certain features (like real-time traffic updates), then losing that connection could mean those features stop working.
Solution: The upcoming 5G technology is set to provide faster and more reliable internet connectivity. This means connected vehicles will have better chances of staying connected to the internet, even in remote areas. It's kind of like upgrading from a patchy, unreliable phone connection to a high-speed, reliable one.
Interoperability: There are many different devices, technologies, and platforms involved in IoT. Getting all these to communicate and work together seamlessly can be a challenge.
Solution: Standards are being developed to improve interoperability in IoT. These include technical standards for how devices communicate, as well as data standards to ensure data can be understood by different systems.
Data Overload: Connected vehicles can generate a huge amount of data. Managing, storing, and processing this data efficiently can be a daunting task.
Solution: Advances in cloud computing and edge computing are helping to manage the data load. Cloud computing provides large amounts of storage and processing power, while edge computing allows for some data processing to be done directly on the devices, reducing the need to transmit and store all data in the cloud.
Regulatory and Legal Issues: As connected vehicle technology is still relatively new, there may be legal and regulatory hurdles. These could include issues around liability in case of self-driving car accidents, or legislation related to data collection and use.
Solution: Governments, regulators, and industry groups are working to develop appropriate legal and regulatory frameworks. This is a complex area and will take time, but progress is being made.
User Acceptance: Not everyone is comfortable with the idea of their car being connected and data being collected. Overcoming these reservations is a challenge for wider adoption of connected vehicle technology.
Solution: Education and transparency are key to addressing user concerns. This includes clear explanations of what data is collected and how it's used, as well as demonstrating the benefits of connected vehicle technology.
Automotive companies and tech firms are actively addressing these issues. Rigorous cybersecurity measures are being implemented to protect user data. Also, the development of 5G technology promises faster, more reliable connectivity, overcoming the limitations of current networks.
Trends and Future Perspectives
As for the future, the possibilities seem limitless. The further advancement of IoT in connected vehicles could lead to fully autonomous cars that communicate with each other to reduce traffic congestion, resulting in greener and more efficient cities. IoT also plays a significant role in the development of smart city infrastructure, with connected vehicles at the heart of it.
Industry experts agree that IoT is a driving force in the automotive industry. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, by 2030, up to 50% of the value of a car could be derived from its connected features.
Exciting times lie ahead in the realm of IoT and connected vehicle technology. The integration of IoT into our vehicles is not just enhancing our driving experience, but it's paving the way for a more connected, efficient, and intelligent future. It's clear that the road ahead is more than just about getting from point A to B, but about creating a journey that's as smart as it is efficient.

