IoT Security: How to Protect Your Connected Devices
How would you like to be locked out of your own house? Or have your heating turned off?
These aren’t hypothetical what-ifs. With the penetration of IoT devices into our everyday life, these incidents are becoming commonplace.
The risk of gaps in IoT device security isn’t just limited to cyber threats. Due to the physical nature of IoT, the security risks now spill over into our personal lives.
How is this happening? And what can we do about it exactly?
What to expect: In this article, we'll explore the evolving landscape of IoT devices and the security concerns that come with them. We'll also provide some tips on security for IoT devices. Finally, we'll answer some frequently asked questions about IoT device security.
IoT devices and security concerns
The world is connected today. As of last year, roughly 63% of the world has strong internet connectivity. And most of the Americas, Europe, Asia, and Australia are thoroughly connected.
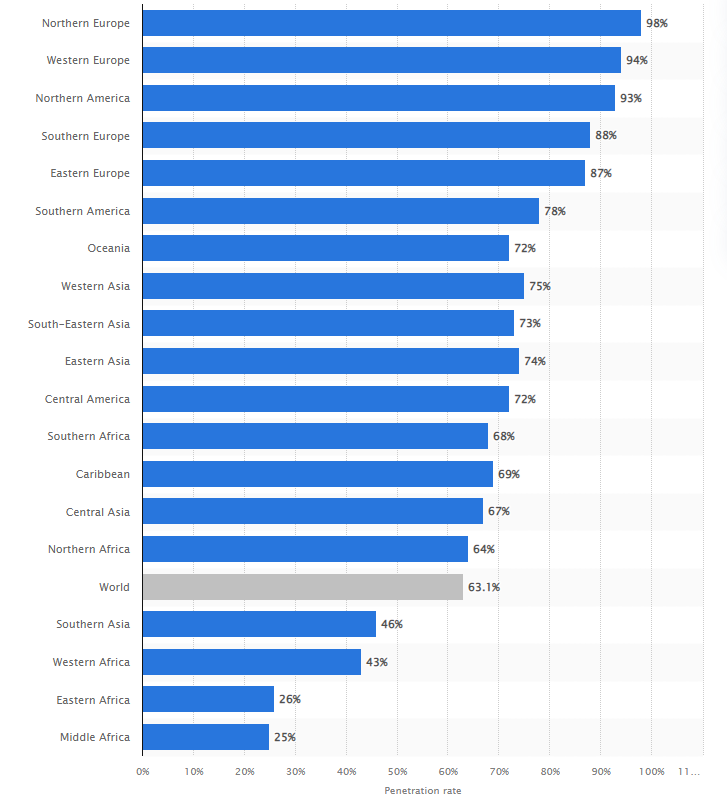
This has directly led to an increase in the adoption of IoT devices in highly connected regions. Home automation, building management, energy consumption, healthcare, transportation, surveillance, and several other crucial industries rely on IoT devices for efficient functioning.
But there are some major risks we face.
According to the 2020 Unit 42 IoT Threat Report, 98% of all IoT traffic is unencrypted, exposing personal and confidential data on the network.
Not just this, but the report also stated,
57% of IoT devices are vulnerable to medium- or high-severity attacks, making IoT the low-hanging fruit for attackers.
These statistics shine a glaring light on the issues associated with IoT security today. Cybersecurity, as a whole, needs to be updated at a breakneck pace. Hackers and attackers are nearly always coming up with new ways to break into private networks.
Conversely, IoT devices don’t even have some basic security features such as encryption on most devices. A big reason for this is the lack of governance when it comes to manufacturing, packaging, and setup of IoT devices and services. As there were no standards to follow up until very recently, most businesses just opt for the cheapest available devices.
Why secure your IoT devices?
It may seem like a good business practice to cut down on costs, but is IoT device security really the place to do it?
- In 2016, the Finnish city of Lappeenranta faced a DDoS attack on its heating controllers which turned off the heating in two major buildings in the city. In warmer climates, this may not be a big deal. But Finland faces some of the harshest winters in the world. So the people in these buildings were left to fend off lethal temperatures.
- The same year, the world saw the Mirai botnet attack, which shut off several large traffic websites such as CNN, Netflix, and Twitter.
But these attacks happened to big cities and business conglomerates. On an individual level, the threats somehow become scarier.
A ‘routine’ hack
In 2019, CNN managed to access security and surveillance footage from across the world of people going on about their routine. This included an Australian family doing their daily chores, a woman feeding her cat in Japan, and a man getting dressed in Moscow.
These security incidents aren’t a one-off and ring the alarm bells for the need to secure your IoT devices, both personal and business.
An internet of sex scandal
Connected sex toys are a big segment for IoT, and there are over 50 million sextech devices in use already.
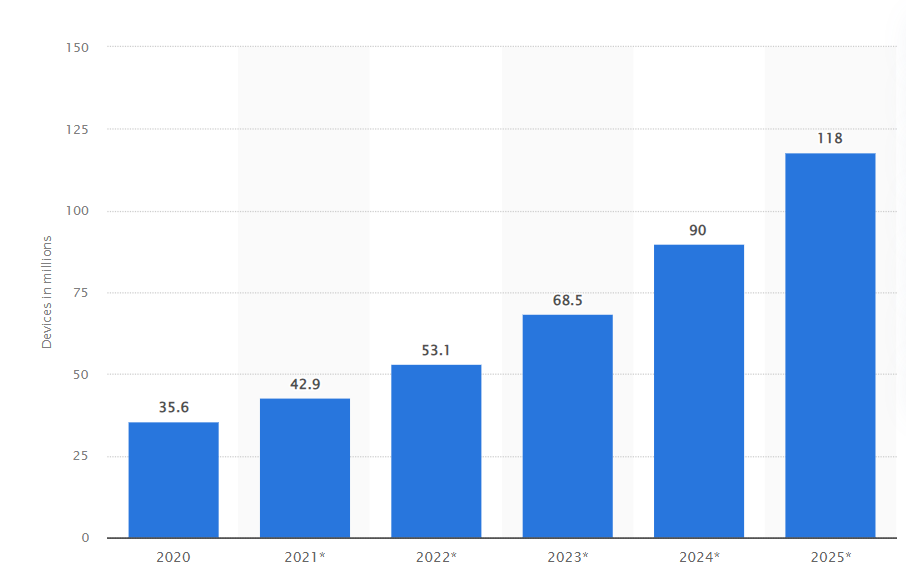
Over 75% of Americans over 18, own a sex toy, and a large number of them are connected.
But what happens when they get hacked?
In 2018, a sex toy database was hacked which led to a leak of all the customer data including explicit images, chat logs, sexual orientation, email addresses, passwords, etc. in clear text.
A smart hotel nightmare
In 2021, a security consultant hacked into a hotel’s smart systems to control the utilities of a neighboring room. While this was to help the hotel, this could easily turn into a nightmarish hotel visit for a guest whose hotel lights, cameras, heating, and sound systems were hacked.
IoT Devices: potential security threats and vulnerabilities
The potential threats in IoT are grave, and even though security experts have been ringing the alarm bells for years, the average person just isn’t aware of the extent.
According to the Unit 42 report, enterprises have several vulnerable devices that need to be secured.
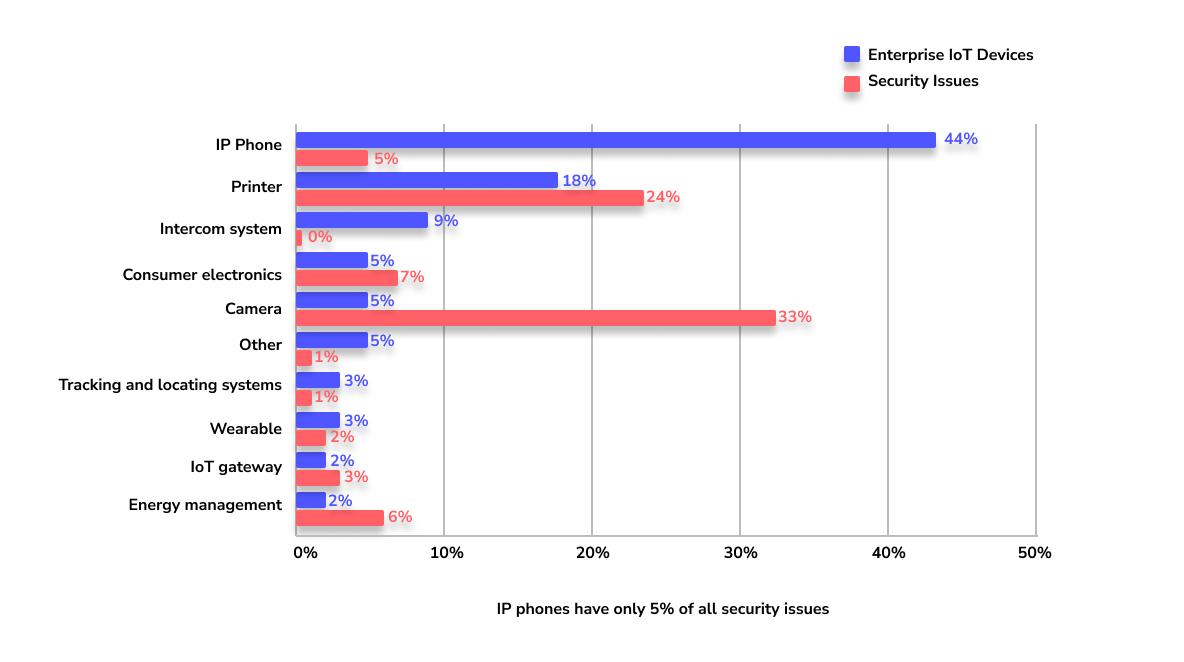
Among this list, cameras are the most vulnerable devices that enterprises use, and printers are a close second.
The report also clarified that exploiting vulnerable devices and using malware to attack are the most common security threats for IoT devices.
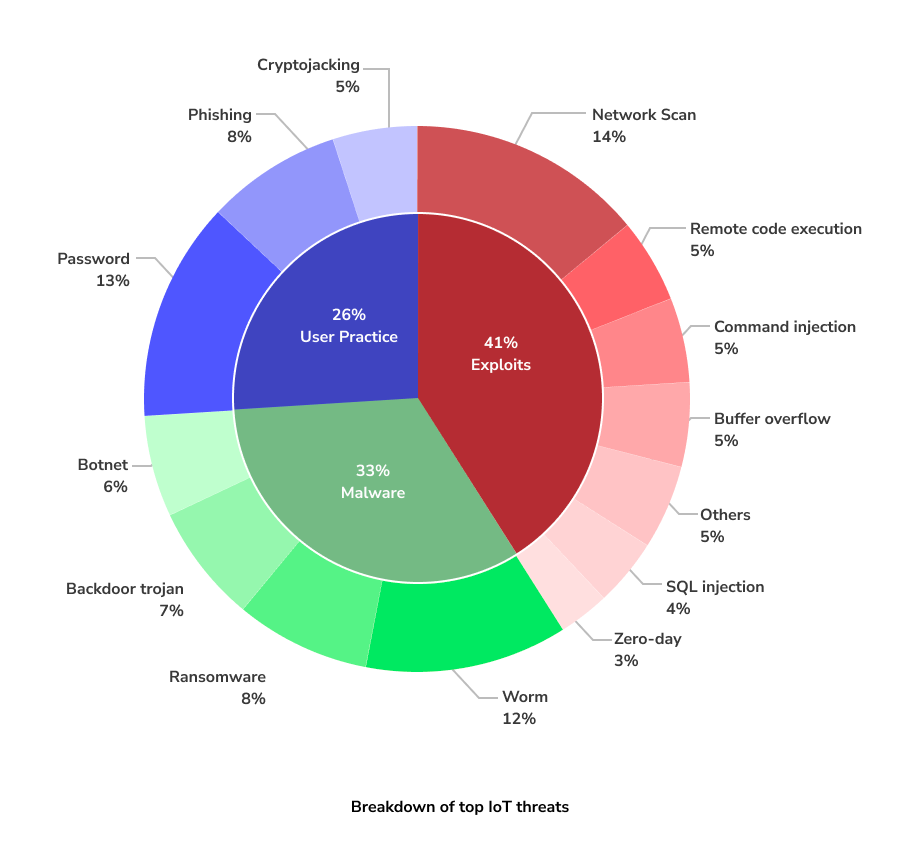
With more connected devices coming up, the potential threats go up, with the likes of
- Growing privacy and data protection concerns.
- Insecure communication due to lack of encryption standards.
- Unupdated devices being hacked.
- Privacy and security of stored data.
- User authentication failure.
IoT Security Challenges
IoT security is not exactly an unknown devil, most people who work with IoT already know of the security concerns.
So why do these concerns go largely unaddressed?
Let us take a look at the reasons.
Dependence on legacy systems
One major challenge facing IoT security is the dependence on legacy systems. Many IoT devices are built on older technologies. These technologies are not equipped with the latest security features, which poses a great risk to the overall network.
This is a unique challenge as a lot of the legacy OS do not offer any new security updates or patches. This also means that even outdated threats and attacks can pose a risk to these devices.
The problem with legacy protocols is that they were designed for devices that remained behind a firewall. For connected devices, these protocols just do not work anymore.
For example, Palo Alto Networks found a vulnerability in the DICOM protocol which allowed attackers to change the header in a DICOM packet and replace the image with an executable file.And given that the antivirus does not scan confidential files, this malware persisted on the network until manually detected.
To address this challenge, organizations should invest in upgrading their legacy systems and ensure that all new devices are built with the latest security standards in mind. However, this brings in further challenges like financial constraints and inertia toward migration.
Open-sourced code
Another challenge is the use of open-sourced code in IoT devices. While open-source code is a crucial resource for developers, it can also be a security risk if not properly managed. Responsible developers tend to modify open-sourced code for securing IoT devices, but this is not the norm.
Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in open-source code to gain access to devices and steal sensitive information.
To mitigate this risk, organizations should ensure that all open-source code used in their devices is properly vetted and updated regularly to address any new vulnerabilities.
Security integration
Security integration is another important aspect of securing IoT devices. Many organizations struggle to effectively integrate security into their IoT systems, resulting in a lack of coordination and oversight.
As IoT devices aren’t always uniform or homogenous in a given project, integrating can be extremely complex.
To address this challenge, organizations should adopt a holistic approach to IoT security and ensure that all security measures are integrated into their overall security strategy. This includes developing security policies and procedures, as well as training employees on connected device security and how to properly manage and secure IoT devices.
Data transmission and storage
Data transmission and storage are major concerns when it comes to IoT security. Many IoT devices collect and transmit sensitive information, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
However, the amount of data that IoT devices generate can be overwhelming and very difficult to manage without proper systems in place.
To protect against data breaches, encryption of all data is crucial. It is also important to store the data in secure, off-site locations. Here, activity logs can prove to be a useful tool to monitor unusual activity and implement incident response plans in case of a security incident.
User authentication
While organizations now understand the importance of security, user authentication is still a vulnerability that is commonly exploited. Many IoT devices do not have built-in authentication mechanisms, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access.
Moreover, individual users still tend to use weak passwords, making their accounts vulnerable.
Implementing strong user authentication protocols for devices, such as multi-factor authentication is a good way to overcome this. Additionally, organizations need to employ the principle of privilege, where access is granted on a need-to-know basis. Finally, imposing a policy for strong passwords can go a long way in terms of security.
Best Practices for IoT device security
Here are some things that you can do to secure your IoT devices from attacks.
Create Strong Passwords
One way to protect your IoT devices is by using strong passwords. A strong password should be at least eight characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. You should never use easily guessed words like "password" or easily accessible personal information like your birthdate.
It is in our nature to pick an easy access key or password so that we can remember it easily. Statista shared a list of the most common passwords used for IoT devices here:
While this is convenient, it is also a massive security risk.
The best way to ensure strong passwords is to use a password manager which generates and saves random passwords. Make sure not to use the password managers which are available on browsers. Instead, invest in a secure password manager.
Use a Secure IoT Platform
A secure well-rounded IoT platform will help you monitor all your devices in one place. This will allow you to keep an eye on the health of your devices, push updates regularly, ensure that all the data transmitted to and from the devices is secured, and that none of the devices are tampered with.
Choosing the right IoT platform can make a big difference in terms of security for your devices.
Thorough Data Encryption
One of the key solutions to ensuring the security of IoT devices is to encrypt data at rest and in transit. Encryption is the process of encoding data so that it can only be accessed by authorized parties with the proper decryption key.
It's also important to use a robust encryption algorithm, such as AES or RSA, which are widely accepted as secure standards. Additionally, organizations should regularly update their encryption keys to ensure that they are not compromised and to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Update Your Devices
It is also important to keep your IoT devices up-to-date with the latest security patches. Manufacturers regularly release security updates to fix vulnerabilities in their products. By keeping your devices updated, you can help protect them against the latest threats.
Verify All New Updates
Software and firmware updates are released to fix known vulnerabilities, add new features, and improve the performance of the device. However, these updates can also introduce new vulnerabilities if they are not properly vetted.
To ensure that software and firmware updates are secure, you need to implement a process for verifying the authenticity and integrity of the updates before they are installed on devices. This process can include checking digital signatures, using a secure update server, and validating the update package.
You should also test the updates in a lab environment before rolling them out to the devices to ensure that they do not cause any unintended consequences or introduce new vulnerabilities.
It is also recommended to only accept updates from trusted sources and to be cautious when downloading updates from third-party websites. By implementing a thorough verification process, organizations can ensure that the software and firmware updates they install on their devices are secure and do not compromise the security of their IoT systems.
Create Unique Credentials
It is not enough to password-protect your devices. You also need to create unique credentials for each one of them. Many IoT devices come with default or easily guessable credentials, such as "admin" for the username and "password" for the password, which can be easily compromised by cybercriminals.
To prevent unauthorized access to devices, unique and complex credentials for each device are crucial. This can be achieved by using a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters for the username and password, and regularly changing the credentials.
Another option is to use a secure authentication protocol, such as multi-factor authentication, which requires multiple forms of identification to access the device. Additionally, there needs to be a process for managing and revoking device credentials. This is important in case a device is lost or stolen, or an employee leaves the organization.
Ways to secure enterprise IoT devices
Securing enterprise IoT devices is crucial to safeguard both the organization's data and its operational integrity. Here are some key strategies and best practices to enhance the security of enterprise IoT devices:
- Change Default Credentials: Many IoT devices come with default usernames and passwords. Always change these to strong, unique credentials before deployment.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Ensure that all devices receive regular firmware and software updates to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Network Segregation: Keep IoT devices on separate network segments from critical business systems to contain potential breaches.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection: Implement firewalls to control the traffic that IoT devices can send and receive. Use intrusion detection systems to monitor for suspicious activities.
- Device Management Solutions: Employ centralized IoT device management platforms to monitor, update, and manage device configurations.
- Use Encryption: Ensure data in transit (and at rest, when applicable) is encrypted to prevent interception.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Turn off any unused features, services, or ports on the IoT device that are not required for its function.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Only allow users access to the IoT devices and data they require for their specific role.
- Regular Audits: Periodically review and assess the security posture of your IoT devices. Check for any devices that are no longer in use, aren't updated, or have vulnerabilities.
- Physical Security: Ensure devices are protected from physical tampering. This includes locking down devices and considering tamper-evident designs.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about the risks associated with IoT devices and the best practices for using them securely.
- Vendor Assessment: Before procuring an IoT solution, evaluate the security features and track record of the vendor. Ensure they adhere to recognized security standards and best practices.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing IoT devices and ensure each device has a unique identity.
- Monitoring and Anomaly Detection: Continuously monitor the behavior of IoT devices and set up alerts for any abnormal patterns or behaviors.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a plan in place detailing how to respond if an IoT device is compromised or behaves anomalously.
Remember, while individual security measures are essential, a multi-layered, holistic approach will offer the best protection for enterprise IoT devices.
The Future of IoT Security
The number of malware attacks on IoT devices has been growing in recent months.
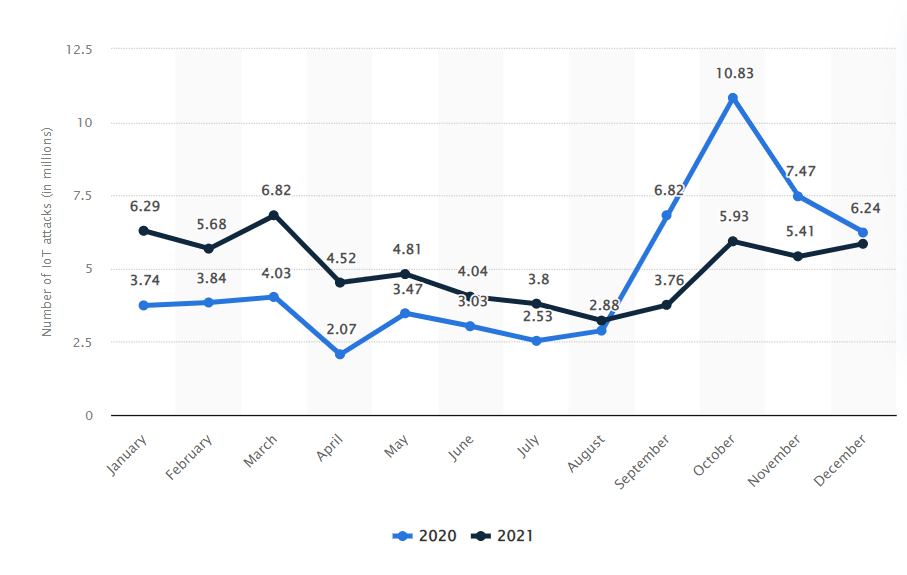
According to Statista, The number of Internet of Things (IoT) attacks in the world reached over 10.8 million in October 2020.
Given these numbers, it is only natural that security practices will also evolve. As of the start of 2023, the industry is witnessing a big push toward Zero Trust practices to make the entire architecture more secure.
Zero Trust is an approach towards security that does not assume trust in any elements of the architecture, be it human or digital. The elimination of presumed trust allows organizations to design systems that continuously verify and validate every process in digital architectures.
The upcoming cybersecurity acts demand that organizations be prepared for any scenario. According to Nader Henein, VP Analyst at Gartner,
“By year-end 2024, Gartner predicts that 75% of the world’s population will have its personal data covered under modern privacy regulations.”
This means that there will be more emphasis on compliance in the coming years, and is a welcome direction for cybersecurity as a whole.
Overall, security is becoming a part of the design itself in IoT-first organizations. Even though security is a serious matter, it is not all doom and gloom. The fact that new security concerns keep cropping up, suggests that IoT is evolving rapidly, and will be responsible for several more technological breakthroughs.
The only way to ride this wave is to secure your IoT projects with reliable IoT solutions, such as Bytebeam. If you would like to know more about how Bytebeam helps you maintain and improve security for your projects, feel free to reach out to us or comment below.
Frequently Asked Questions
How should you secure your IoT devices?
There are various ways to secure your IoT devices. The most common ways being: change default passwords, regularly update software/firmware, use strong encryption for data, connect them to a secure network, and disable unnecessary features. Think of it as locking and regularly checking your digital doors and windows.
Why is it hard to secure IoT devices?
Securing IoT devices is challenging because they're diverse, often have weak default settings, might lack update options, and are designed with more focus on functionality than security. It's like having many types of doors but not all having good locks.
How to secure IoT devices in an enterprise?
For enterprises: Set strong, unique passwords for devices. Regularly update device software. Use secure networks with firewalls. Segregate IoT devices from critical business systems. Train employees about risks and best practices. Think of it as guarding your company's digital entry points.

